Beginning with Psychiatry vs Psychology: Understanding the Key Differences, the narrative unfolds in a compelling and distinctive manner, drawing readers into a story that promises to be both engaging and uniquely memorable.
In this exploration of Psychiatry vs Psychology, we will delve into the fundamental disparities between these two fields, shedding light on their distinct approaches towards mental health and well-being.
Psychiatry vs Psychology
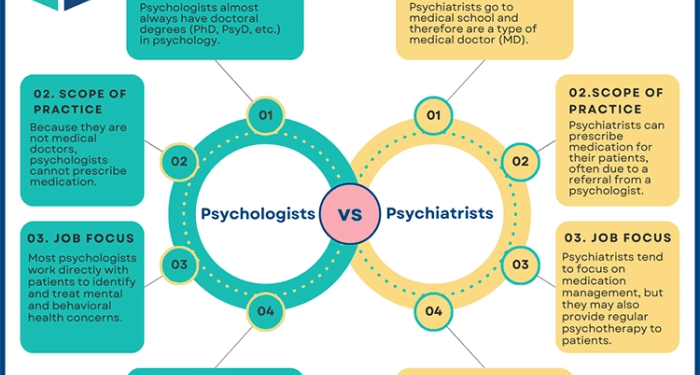
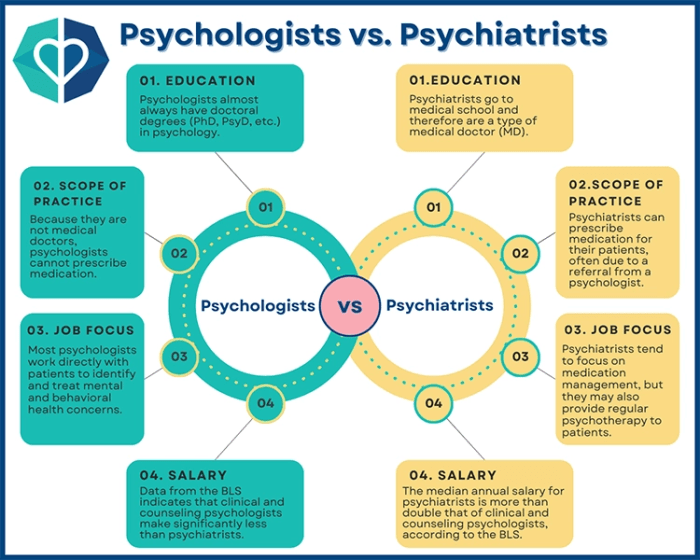
Psychiatry and psychology are two distinct fields that focus on mental health and well-being, but they differ in their approaches and methods.Psychiatry:Psychiatry is a branch of medicine that deals with diagnosing, treating, and preventing mental illnesses. Psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medications and utilize a variety of therapeutic techniques to address mental health issues.
They often work with individuals who have severe mental disorders such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depression.Psychology:Psychology, on the other hand, is a field that studies human behavior and mental processes. Psychologists use various therapeutic approaches to help individuals overcome challenges, improve their mental health, and enhance their overall well-being.
They may specialize in areas such as clinical psychology, counseling psychology, or school psychology.
Consulting a Psychiatrist vs Psychologist
- When to consult a psychiatrist:
Individuals experiencing severe mental health conditions like psychosis, severe depression, or bipolar disorder may benefit from seeing a psychiatrist who can provide medication management and more intensive treatment.
- When to consult a psychologist:
People facing challenges such as relationship issues, stress management, or behavioral problems may find it helpful to consult a psychologist for therapy sessions and psychological interventions that focus on coping strategies and personal growth.
Education and Training
Becoming a psychiatrist or a psychologist requires a significant amount of education and training. Let's delve into the specific paths one must take to enter each field.
Educational Paths for Psychiatrists
To become a psychiatrist, one must first complete a bachelor's degree in a related field, such as psychology or biology. After obtaining a bachelor's degree, aspiring psychiatrists must attend medical school to earn a Doctor of Medicine (M.D.) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) degree.
Following medical school, psychiatrists must complete a four-year residency program in psychiatry.
Educational Paths for Psychologists
Psychologists typically start by earning a bachelor's degree in psychology or a related field. This is followed by a graduate degree in psychology, such as a Master's or Doctoral degree. Those pursuing a Doctoral degree can choose between a Ph.D.
in Psychology or a Psy.D. (Doctor of Psychology) degree. Additionally, psychologists must complete a supervised internship and obtain a license to practice.
Types of Degrees, Certifications, and Licenses
Psychiatrists hold an M.D. or D.O. degree, enabling them to prescribe medication and provide medical treatments. They must also obtain a medical license to practice. Psychologists, on the other hand, hold either a Ph.D.
or Psy.D. degree, allowing them to provide therapy and counseling services. Psychologists must also obtain a license to practice independently.
Duration and Focus of Training Programs
The training path for psychiatrists is longer due to the medical school requirement. Psychiatrists typically spend four years in medical school, followed by a four-year residency in psychiatry. In contrast, psychologists usually spend around 5-7 years in graduate school, with additional time spent on internships and post-doctoral training.
The focus of training for psychiatrists is more medical and biological, while psychologists focus more on psychological theories and therapeutic techniques
Treatment Approaches
When it comes to treatment approaches, psychiatrists and psychologists utilize different methods tailored to their expertise and training.
Medication Management by Psychiatrists
Psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medications to help manage mental health conditions. They often use a combination of therapy and medication to address symptoms effectively. Medications prescribed by psychiatrists can include antidepressants, antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, and anti-anxiety drugs.
These medications can play a crucial role in managing conditions like depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.
Therapy Techniques by Psychologists
Psychologists primarily use psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, to help individuals overcome mental health challenges. There are various types of therapy techniques employed by psychologists, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), psychodynamic therapy, and humanistic therapy.
These therapy approaches focus on exploring thoughts, emotions, behaviors, and past experiences to promote positive changes and improve overall well-being.
Scope of Practice
In clinical settings, psychiatrists and psychologists play distinct but complementary roles in providing mental health care. While psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medication, psychologists focus on psychotherapy and psychological assessment.
Psychiatrists
- Psychiatrists are trained medical doctors specializing in mental health.
- They diagnose and treat mental health disorders, often utilizing medication management.
- Common issues addressed by psychiatrists include mood disorders, anxiety disorders, psychotic disorders, and substance abuse.
- They may also work with patients experiencing severe mental illness or crisis situations.
Psychologists
- Psychologists hold advanced degrees in psychology and are trained in psychotherapy.
- They provide therapy, counseling, and psychological testing to help patients address emotional and behavioral issues.
- Psychologists often work with individuals dealing with issues like depression, trauma, relationship problems, and stress management.
- They may specialize in areas such as child psychology, forensic psychology, or health psychology.
Complementary Roles
Psychiatrists and psychologists often collaborate to provide comprehensive mental health care.
- Psychiatrists can prescribe medication to manage symptoms, while psychologists offer therapy to address underlying issues.
- Together, they can create a more holistic treatment plan for patients with complex mental health needs.
- This collaborative approach allows for a more personalized and effective treatment strategy.
Last Word
In conclusion, the comparison between Psychiatry and Psychology highlights the importance of both disciplines in the realm of mental health care, emphasizing how their collaborative efforts lead to comprehensive and effective treatment solutions for individuals.
Query Resolution
What is the main difference between psychiatry and psychology?
Psychiatry deals with diagnosing and treating mental illnesses using medication and other medical interventions, while psychology focuses on understanding human behavior and mental processes through therapy and counseling.
What qualifications are needed to become a psychiatrist or psychologist?
To become a psychiatrist, one needs to complete medical school and a psychiatry residency, while a psychologist typically requires a doctoral degree in psychology and supervised clinical experience.
How do psychiatrists and psychologists complement each other in mental health care?
Psychiatrists can prescribe medication and provide medical treatments, while psychologists offer therapy and counseling services, creating a holistic approach to mental health treatment.